Template helpers
Diem provides handy template helpers, which make code cleaner and more concise
Like for symfony, Diem template language is PHP, because PHP is a template language.
PHP written templates can become verbose, difficult to read and hard to maintain. And writing tags by hand is prone to errors.
Diem proposes some handy helpers to make the view layer more concise.
- all generated code is XHTML 1.1 Strict compliant.
- HTML attributes are properly escaped
- all helpers are object oriented and managed by the Service Container. You are encouraged to extend them (for which an example can be found here).
- Helpers are tested for stability and performance
Use them... or not
Use of Diem helpers is optional. You can decide not to use them, use them partially, or use your own template helpers.
Access to helpers
Helper functions are available in all templates and partials.
From an action or a component, you can call $this->getHelper() to get the same methods.
// in a template: _link($record) // in an action / component: $this->getHelper()->link($record) // other places, if you have a $context instance $context->getHelper()->link($record) // other places, if you don't have a $context instance dm::getHelper()->link($record)
When accessed with the helper instance, the methods are not prefixed with an underscore.
Tag helpers
_tag : create a tag
// <p>Some text</p> _tag('p', 'Some text')
CSS expressions
You can add CSS expressions to the tag name, exactly the same way you do with a stylesheet or a jQuery selector.
// <p class="info">Some text</p> _tag('p.info', 'Some Text') // <p class="info green">Some text</p> _tag('p.info.green', 'Some Text') // <p id="description" class="info green">Some text</p> _tag('p#description.info.green', 'Some Text')
The last one in CSS: p#description.info.green
And as a jQuery selector: $('p#description.info.green')
Inline attributes
You can pass HTML attributes after the tag name.
// <p class="info" lang="es">Eso me gusta</p> _tag('p.info lang=es', 'Eso me gusta')
Array attributes
You can pass HTML attributes with an array.
// <p class="info" lang="es">Eso me gusta</p> _tag('p.info', array('lang' => 'es'), 'Eso me gusta')
Json attribute
You can pass json data to an HTML element. The jQuery metadata plugin allow to use it with JavaScript.
// <p class="info { \"version\": \"5.0\" }">Diem tag</p> _tag('p.info', array('json' => array('version' => '5.0')), 'Diem tag')
Nested tags
You can nest the generated tags.
// <div class="wrapper"><p class="info">Some text</p></div> _tag('div.wrapper', _tag('p.info', 'Some text'))
It's better to indent nested tags:
// <div class="wrapper"> // <p class="info"> // Some text // <span>and even more</span> // </p> // </div> _tag('div.wrapper', _tag('p.info', 'Some text'. _tag('span', 'and even more') ) )
The great thing with _tag imbrication is that you just can't break html validity. If you forget to close a tag ( with a closing parenthesis ), then PHP throws an error.
Merge with HTML
You can give HTML code to a _tag.
// <p class="info"><span>Some Text</span></p> _tag('p.info', '<span>Some text</span>')
_open : open a tag
_open shares the same features than _tag, but it only opens the tag
// <p> _open('p') // <p id="description" class="info green"> _open('p#description.info.green') // <p class="info" lang="es"> _tag('p.info', array('lang' => 'es'))
_close : close a tag
// </p> _close('p')
_link : create a link
This one is very useful. Links are something serious.
External links
// <a href="https://diem-project.org">Link text</a> _link('https://diem-project.org')->text('Link text')
CSS expressions
You can add CSS expressions to the link with the ->set() method, with exactly the same syntax than in a stylesheet or a jQuery selector.
// <a id="github" class="scm_repo big" href="http://github.com">github</a> _link('http://github.com')->set('#github.scm_repo.big')->text('github')
Internal links
As our site urls are dynamic, we can no more work with pure HTML.
We will now compare the Diem syntax with the symfony one.
Link to a page with module/action
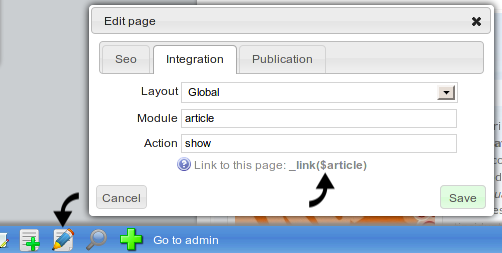
Each Diem page is identified with a module and action. To know module and action of a page, go on the page and click the edit page button in the front tool bar.

Suppose we have a site with products. We will link to the products list.
// symfony link_to('Products', 'product/list') // Diem _link('product/list')->text('Products') // if you don't give the text, it will use the page name: _link('product/list')
Link to a symfony action
Sometimes we want do display a link not to a page but to a symfony action.
The syntax is +/module/action
// symfony link_to('Logout', 'dmUser/signout') //Diem _link('+/dmUser/signout')->text('Logout')
Link to a record
If a record has a dedicated page, we can link to this page with the record.
// symfony link_to($product->name, 'product/show?id='.$product->id) // Diem _link($product)
Add an automatic title to all links
Titles are important for accessibility and SEO. But filling manually all of them is difficult.
In the configuration panel, Interface tab, you can choose to enable "Link use page title". If enabled, all internal links will get the page title as their title attribute.
Links to the current page
Transform to span
A link to the the current page shouldn't exist : clicking on it does nothing.
In the configuration panel, Interface tab, you can choose to enable "Link current span". If enabled, links to the current page will be transformed into spans.
You also can change this behavior when creating a link:
_link(...)->currentSpan(true) // becomes a span if link href is the current href _link(...)->currentSpan(false) // will never become a span
A "link" css class is added to all links, a and span.
Add a current css class
Links to the current page get a current css_class.
// We are currently on the homepage _link('@homepage') // <span class="link dm_current">Home</span>
Configure current class for one link
_link('@homepage')->currentClass('my_current_class')
Configure current class for all links
apps/front/config/dm/services.yml
parameters: link_tag_page.options: current_class: my_current_class
Links to a parent page
Sometimes we want to add style to links that target a page that is a parent of the current page.
For example, we are on a product page, we want links to the product category page to get a parent class.
By default, links to a parent page get a parent css_class.
// We are currently on a product page _link($product->Category) // <a class="link dm_parent" href="/the-category">The category</a>
Configure parent class for one link
_link('@homepage')->parentClass('my_parent_class')
Configure parent class for all links
apps/front/config/dm/services.yml
parameters: link_tag_page.options: parent_class: my_parent_class
Links to an inactive page
Pages can be marked as "Not available". When a link targets such a page, it will be changed to a span, excepted if the user has the "site_view" permission.
$page->isActive = true; _link($page) //<a class="link" href="...">Page name</a> $page->isActive = false; _link($page) //<span class="link dm_inactive">Page name</span>
Links to external websites
Some customers require than all external links get a target="_blank".
In the configuration panel, Interface tab, you can choose to enable "Link external blank". If enabled, links to external websites get a "_blank" target.
More examples
// link to homepage _link() // link with title _link()->title('Back to home') // link with target=_blank _link('http://far.com')->target('blank') // or ->target('_blank') // link to a page with an anchor ( url#the_anchor ) _link('module/action')->anchor('the_anchor') // link to a product with query params ( product?display=all ) _link($product)->param('display', 'all') // link with json data _link($product)->json(array('var1' => 'value')) // link to another culture _link('+/dmCore/selectCulture')->param('culture', 'es')->text('Spanish'); // just get the $product page url $url = _link($product)->getHref() // get the $product page url from a component or an action $url = $this->getHelper()->link($product)->getHref() // get the $product page url with uri prefix $url = _link($product)->getAbsoluteHref() // very complex link _link($product) ->text(__('Translated text')) ->set('#my_id.a_class.another_class name=my_name') ->title('My title') ->param('var', 'value') ->param('another_var', 'another value') ->params(array('var1' => 1, 'var2' => 33)) ->anchor('to_this_anchor') ->target('blank') ->currentSpan(true) // become a span if link href is the current href
_media : create a media
Usefull to display images.
You can also use video, audio and flash medias with the dmFlowPlayerPlugin.
Display a file media
// <img src="/theme/images/logo.jpg" alt="Diem logo" /> _media('logo.jpg')->alt('Diem logo')
CSS expressions
You can add CSS expressions to the media with the ->set() method, with exactly the same syntax than in a stylesheet or a jQuery selector.
// <img src="/theme/images/logo.jpg" id="logo_image" class="logo big" alt="Diem logo" /> _media('logo.jpg')->set('#logo_image.logo.big')->alt('Diem logo')
Display a record image
Suppose we have products in our website. In the data model, Product has a relation with DmMedia:
Product:
columns:
name: { type: string(255)
image_id: { type: integer }
relations:
Image:
class: DmMedia
local: image_id
We can easily display the product image:
// <img src="/uploads/product/my_image.jpg" width="400" height="300" alt="Product name" /> _media($product->Image)->alt($product->name)
Note that the width and height attributes are automatically filled with the image size. This helps the browser to display the page faster.
Resize the record image
Create image thumbnails should be the designer's responsibility. With _media, it's made as easy as:
//<img src="/uploads/product/.thumbs/my_image.jpg" width="200" height="150" /> _media($product->Image)->size(200, 150)
A thumbnail will be generated on the fly, and stored on the filesystem to increase performance.
By default, if the image ratio is not respected, the image will be centered in a smart way. It generally does the trick. You can choose another default resize method in the configuration panel, Interface tab.
More examples:
_media($product->Media)->width(400)// height will be calculated _media($product->Media)->height(400) // width will be calculated _media($product->Image)->method('scale') // change the resize method for this image.
Resize methods
Several methods are available when resizing an image. Imagine we are resizing a 200x100 image:
// will resize the image without altering the ratio nor cropping it, // to fit in the given space. Produces a 100x50 image. _media($product->Image)->size(100, 100)->method('scale'); // will resize the image without altering the ratio nor cropping it, // to fit in the given space. Fills blank space with a background color to make the image size as requested. Produces a 100x100 image. _media($product->Image)->size(100, 100)->method('fit')->background('#FFFFFF'); // will resize the image by altering the ratio, // to fit in the given space. Produces a 100x100 image. _media($product->Image)->size(100, 100)->method('inflate'); // will crop to the center of the image. Produces a 100x100 image. _media($product->Image)->size(100, 100)->method('center'); // will crop to the top of the image. Produces a 100x100 image. _media($product->Image)->size(100, 100)->method('top'); // will crop to the bottom of the image. Produces a 100x100 image. _media($product->Image)->size(100, 100)->method('bottom'); // will crop to the left of the image. Produces a 100x100 image. _media($product->Image)->size(100, 100)->method('left'); // will crop to the right of the image. Produces a 100x100 image. _media($product->Image)->size(100, 100)->method('right');
You can change the default resize method in the configuration panel.
Add an overlay to the image
You can add overlays ( like a watermark, for example ) on images:
_media($product->Image)->overlay(_media('watermark.png'), 'center') // or _media($product->Image)->overlay(_media('watermark.png'), 'top-left')
The watermarked image will be generated on the fly and stored on the filesystem.
Apply filters on the image
You can apply filters on images:
_media($product->Image)->filter('greyscale')
The filtered image will be generated on the fly and stored on the filesystem.
Change compression quality
JPG images can be compressed with a quality factor between 10(poor) and 100(high)
_media($product->Image)->quality(90)
You can change the default image quality in the configuration panel, Interface tab.
More examples
// link to a product, with the product image _link($product)->text(_media($product->Media)); // get the resized image src $src = _media($product->Image)->size(300, 300)->getSrc(); // get the resized image src from an action or a component $src = $this->getHelper()->media($product->Image)->size(300, 300)->getSrc(); // very complex case _media($product->Image) ->set('.product_image.big') ->alt($product->name) ->size(600, 600) ->filter('greyscale') ->overlay(_media('watermark.png')->size(100, 100), 'bottom-right') ->quality(95)
Form helpers
Symfony way to display forms is great, and enough extensible to make it even greatest.
We will see here Diem additions to form rendering.
The lazy way
echo $form;
It displays a full form with form open tag, widgets labels, fields and errors, the submit tag and the form close tag.
Open a form
// <form action="/contact-us" method="post"> $form->open();
CSS expressions
You can add CSS expressions to the form tag, with exactly the same syntax than in a stylesheet or a jQuery selector.
// <form id="contact_form" class="big blue" action="/contact-us" method="post"> $form->open('#contact_form.big.blue');
Inline attributes
You can pass inline attributes, for example to change the action parameter value. By default, the action targets the current page.
// <form class="big" action="another/action" method="get"> $form->open('.big action=another/action method=get')
Display a form widget
In the view layer, a form widget is composed of three parts : the label, the field and the error message.
// <label for="contact_form_email" class="label">Email</label> // <input type="text" id="contact_form_email" class="required" name="contact_form[email]"/> // <ul class="error_list"><li>Required.</li></ul> $form['email']->label()->field()->error()
Of course, the error message will be written only if the field value is not valid.
You may display only one part, or reverse parts order.
echo $form['email']->field() // displays only the input field echo $form['email']->label()->error() // displays the label then the error
Widget label
// <label for="contact_form_email" class="label">Email</label> $form['email']->label()
Label text
You can change the label text by passing it as the first argument :
// <label for="contact_form_email" class="label">Your email address</label> $form['email']->label('Your email address')
CSS expressions
You can add CSS expressions to the label tag, with exactly the same syntax than in a stylesheet or a jQuery selector.
// <label for="contact_form_email" class="big red label">Your email address</label> $form['email']->label('Your email address', '.red.big')
Widget field
The field is where user enters data : it may be an input, a textarea, a select... When writing template we don't care what it is.
// <input type="text" id="contact_form_email" class="required" name="contact_form[email]"/> $form['email']->field()
CSS expressions
You can add CSS expressions to the field tag, with exactly the same syntax than in a stylesheet or a jQuery selector.
// <input type="text" id="contact_form_email" class="tiny grey required" name="contact_form[email]"/> $form['email']->field('.tiny.grey');
Widget error
The error is displayed when user submitted an invalid value.
// <ul class="error_list"><li>Required.</li></ul> $form['email']->error()
Render the submit tag
// <input class="submit" type="submit" value="Send"/> $form->submit('Send');
CSS expressions
You can add CSS expressions to the submit tag, with exactly the same syntax than in a stylesheet or a jQuery selector.
// <input id="form_submit" class="big submit" type="submit" value="Send"/> $form->submit('Send', '#form_submit.big);
Close a form
// </form> $form->close()
Complete example
Here is a way to display a contact form :
// open the form tag with a contact_form css class echo $form->open('.contact_form'); // open a ul tag echo _tag('ul', // open a li tag and write name label, field and error message inside _tag('li', $form['name']->label()->field()->error()). // same with email _tag('li', $form['email']->label()->field()->error()). // change the label text for topic _tag('li', $form['topic']->label('What is it about ?')->field()). _tag('li', $form['body']->label('Your message')->field()) ); // render hidden fields like the CSRF protection echo $form->renderHiddenFields(); // change the submit button text echo $form->submit('Send'); // close the form tag echo $form->close();
See also
There is a Tutorial about how to add a form on your site.
Questions and Feedback
If you need support or have a technical question, you can
- Get help with the Google Group
- Get help with the Forum
- Come and chat on the #diem IRC channel on freenode
The documentation is hosted on GitHub. Feel free to submit issues and patches!
