Writer tips
Tools and tips for content writers
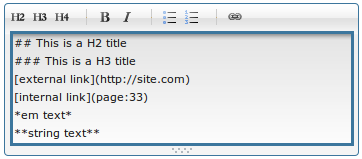
Markdown editor
The markdown editor is the default text editor in Diem. It allows to write for the web in an easy and secure way.
As no HTML code is allowed inside, we can ensure the site HTML code will never get broken.
As no style options are available, only the CSS writer can decide how the generated HTML is styled.
Links
The markdown syntax for links is:
[link text](url)
External links
Select the text you want to transform onto a link, then click the  button.
button.
It will generate:
[link text](http://site.com/page)
Internal links
When creating a link to an internal page, you should never write the page url. Because the page url may change later, and it would result on a broken link.
Instead, when you create a internal link in a markdown editor, please use the PAGES panel:
- Select the text you want to transform onto a link in the markdown editor.
- Open the page panel on the left.
- Browse the page tree, find the page and drag & drop it into the markdown editor.
It will generate:
[link text](page:33)
This way, even if the page url change later, the link gets updated automatically.
Title
You can add a title attribute to external links:
[the link text](http://site.com/page "the link title")
<a href="http://site.com/page" title="the link title">the link text</a>
and internal links:
[the link text](page:33 "the link title")
<a href="/page/url" title="the link title">the link text</a>
Anchor
You can use anchors both on external links:
[the link text](http://site.com/page#anchor)
<a href="http://site.com/page#anchor">the link text</a>
and internal links:
[the link text](page:33#anchor)
<a href="/page/url#anchor">the link text</a>
Query parameters
You can add query parameters both on external links:
[the link text](http://site.com/page?var=val)
<a href="http://site.com/page?var=val">the link text</a>
and internal links:
[the link text](page:33?var=val)
<a href="/page/url?var=val">the link text</a>
Attributes
You can add id and classes to the link, with a CSS expression:
[the link text](http://site.com/page #my_id.a_class)
<a href="http://site.com/page" id="my_id" class="a_class">the link text</a>
[the link text](page:33 #my_id.a_class)
<a href="/page/url" id="my_id" class="a_class">the link text</a>
Complete example
Let's create a complex internal link with a title, an anchor, query parameters, and id and two classes:
[link text](page:33?var=val#my_anchor "my title" #my_id.class1.class2)
<a href="/page/url?var=val#my_anchor" title="my title" id="my_id" class="class1 class2">link text</a>
Images
The markdown syntax for image inclusion is:

Internal image
- Click in your markdown text the place where you want to add an image.
- Open the media panel on the right.
- Browse the media tree, find the image and drag & drop it into the markdown editor.
It will generate:

External image
You can also use an url as the image source:

Alt
Giving your images an alternative text value is a very good practice.

<img src="/uploads/sflogo.jpg" alt="symfony logo" />
Attributes
You can add id and classes to the image, with a CSS expression:

<img src="/uploads/sflogo.jpg" id="my_id" class="a_class" alt="symfony logo" />
Size
You can resize the image.
Specify width and height:

<img src="/uploads/sflogo.jpg" width="300" height="200" alt="symfony logo" />
Specify only width:

<img src="/uploads/sflogo.jpg" width="300" alt="symfony logo" />
Specify only height:

<img src="/uploads/sflogo.jpg" height="200" alt="symfony logo" />
Square image, same width and height:

<img src="/uploads/sflogo.jpg" width="300" height="300" alt="symfony logo" />
Complete example
Let's create an internal image with alt text, an id, two classes, width and height:

<img src="/uploads/sflogo.jpg" id="my_id" class="class1 class2" width="300" height="200" alt="symfony logo" />
Questions and Feedback
If you need support or have a technical question, you can
- Get help with the Google Group
- Get help with the Forum
- Come and chat on the #diem IRC channel on freenode
The documentation is hosted on GitHub. Feel free to submit issues and patches!
