Create a plugin
Diem plugins are symfony plugins, easy to create and reuse
Module based plugin
In this example we will create a simple blog plugin, intelligently called "dmSimpleBlogPlugin".
First, enable it in
config/ProjectConfiguration.class.php
class ProjectConfiguration extends dmProjectConfiguration { public function setup() { parent::setup(); $this->enablePlugins(array( 'dmSimpleBlogPlugin' )); // ...
Plugin structure
Let's create a minimal plugin structure in our project:
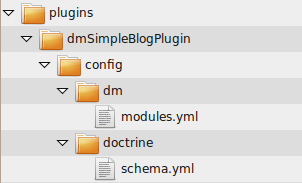
schema.yml
DmSimpleBlogPost:
actAs: [ Timestampable, DmSortable, DmVersionable ]
columns:
name: { type: string(255), notnull: true }
resume: { type: string(255) }
text: { type: clob, extra: markdown }
is_active: { type: boolean, notnull: true, default: true }
created_by: { type: integer }
relations:
Author:
class: DmUser
local: created_by
foreignAlias: DmSimpleBlogPosts
onDelete: SET NULL
DmSimpleBlogComment:
actAs: [ Timestampable ]
columns:
post_id: { type: integer, notnull: true }
name: { type: string(255), notnull: true }
text: { type: clob }
is_active: { type: boolean, notnull: true, default: true }
relations:
Post:
class: DmSimpleBlogPost
local: post_id
foreignAlias: Comments
onDelete: CASCADE It's a good pratice to prefix the plugin models with Dm%PluginName%.
modules.yml
Content:
"Simple Blog":
dmSimpleBlogPost:
name: Blog Post
page: true
components:
list:
show:
dmSimpleBlogComment:
name: Blog Comment
components:
listByBlogPost:
filters: [ dmSimpleBlogPost ]
form: It's a good pratice to prefix the plugin modules with dm%PluginName%.
Code generation
php symfony doctrine:generate-migrations-diff
php symfony doctrine:migrate
php symfony dm:setup Now the plugin is ready.
Admin and front modules have been created in the plugin dir. Customize them as you do for a normal project.
Unit testing your plugin
Enable plugin testing
The first thing to do is to connect your plugin tests to your project by using the setupPlugins method in your ProjectConfiguration.class.php file.
config/ProjectConfiguration.class.php
public function setupPlugins() { $this->pluginConfigurations['dmSimpleBlogPlugin']->connectTests(); }
Create the test files
Then create a test/unit directory into your plugin directory. In this directory, you will create a dmSimpleBlogTest.php file.
test/unit/dmSimpleBlogTest.php
require_once(dirname(__FILE__).'/helper/dmSimpleBlogUnitTestHelper.php'); $helper = new dmSimpleBlogUnitTestHelper(); $helper->boot(); $t = new lime_test(); $t->comment('Testing dmSimpleBlog plugin');
You've certainly noticed that we include a file (dmSimpleBlogUnitTestHelper.php) under a directory called helper. This file will be used to bootstrap the unit test.
So let's create a helper directory under your test/unit directory, and put the dmSimpleBlogUnitTestHelper.php in it.
test/unit/helper/dmSimpleBlogUnitTestHelper.php
require_once(getcwd() .'/config/ProjectConfiguration.class.php'); require_once(dm::getDir().'/dmCorePlugin/test/unit/helper/dmUnitTestHelper.php'); class dmNewsUnitTestHelper extends dmUnitTestHelper { protected $limeTest; public function setLimeTest(lime_test $t) { $this->limeTest = $t; } }
Quite simple isn't it ? It just extends the Diem unit test base class. You can use this class for whatever you want. For example, it can be a good place
to create the objects needed for your test. Then you just have do like usual for writing your unit tests the symfony way.
Questions and Feedback
If you need support or have a technical question, you can
- Get help with the Google Group
- Get help with the Forum
- Come and chat on the #diem IRC channel on freenode
The documentation is hosted on GitHub. Feel free to submit issues and patches!
